Salesforce Service Cloud Certification Study Guide : Luke Freeland
by: Luke Freeland
blow post content copied from Blog
click here to view original post
It’s been a while since I’ve done a certification and Service Cloud seemed like a good one because it’s the second most used “cloud” after Sales Cloud. Also, I’ve worked with pieces of it and would like to round out my knowledge. December 10, 2020 is my exam date. Here’s my study guide for it.
Audience Description
A Salesforce Certified Service Cloud Consultant designs and deploys solutions that support customer business processes and requirements using Salesforce applications. The consultant has experience designing solutions using the Service Cloud functionality and can lead the implementation of these solutions within a customer organization. The consultant has both contact center industry experience and expertise in Salesforce applications including the knowledge needed to implement multiple applications in common customer scenarios.
Salesforce Certified Service Cloud Consultants are interested in demonstrating their expertise as cloud computing implementation consultants with a specialty in the contact center domain. The Salesforce Certified Consultant has 2 to 5 years of experience as a senior business analyst and has developed the skills outlined below:
– Experience managing implementation projects
– Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
– Deep knowledge of Salesforce product lines
– Solid understanding of internet technologies and cloud computing
– Solid understanding of data management and database concepts
– Familiarity with the software development lifecycle
– Ability to:
– Design and implement successful solutions
– Anticipate and mitigate risk
– Meet and manage customer expectations
– Increase customer confidence
– Consistently deliver effective business solutions
– Manage solution delivery and any issues that arise
– Build solutions that are scalable and maintainable
– Set up change management practices to ensure long-term solution success
– Troubleshoot and resolve issues
– Prioritize and escalate customer issues
https://ift.tt/2JRorA9
Exam Outline
Industry Knowledge – 10%
- Explain the factors that influence key contact center metrics, KPIs, and business challenges.
- Explain the use cases and benefits for different interaction channels.
- Compare and contrast the different types of contact centers and their business drivers (help desk, product support, telesales, service, field service/depot repair, B2C, B2B, etc.).
- Identify the benefits of a Knowledge Base.
Implementation Strategies – 15%
- Given a scenario, determine how to facilitate a successful consulting engagement (plan, gather requirements, design, build, test, and document)
- Given a scenario, determine appropriate contact center licensing and deployment strategies.
Service Cloud Solution Design – 16%
- Given a scenario, analyze customer requirements to determine an appropriate solution design considering capabilities, limitations, and design trade-offs.
- Distinguish the key components that contribute to performance optimization within a design.
- Given a scenario, understand the use cases and benefits for implementing CTI, Communities, and Field Service Lightning.
Knowledge Management – 9%
- Explain the knowledge article lifecycle including creation, publishing, consumption, and feedback.
- Given business process requirements, determine the appropriate approach to manage Knowledge adoption and maintenance.
- Given a set of requirements, determine how to configure data categories, article record types, articles, and publishing workflow.
- Understand the key factors to consider when implementing a Knowledge data migration strategy.
- Given a scenario, describe the considerations when migrating from Knowledge to Lightning Knowledge.
Interaction Channels – 10%
- Describe the use cases and functionality for each interaction channel (communities, mobile, phone, email, web, chat, SOS/video channel, and social media.)
- Given business process requirements, determine the appropriate approach to case submission.
- Explain the design considerations (user interface, user profiles, objects to expose, sharing model, reporting, etc.) and best practices when configuring an interaction channel solution (mobile, phone, email, web, chat, or social media).
Case Management – 15%
- Given a set of requirements, design a case management solution from case creation to closure including case assignment, case escalation, case resolution, and case disposition.
- Describe the relationships between cases and other areas such as assets, entitlements, work orders, Communities, Live Agent, and Knowledge.
- Given a set of KPIs, determine the appropriate case management solution.
- Explain the capabilities, use cases, and how to configure the service entitlements and milestones in Salesforce.
- Explain the use cases, capabilities, and limitations of Service Cloud automation (Flow, process builder, quick actions, macros, quick text).
- Identify use cases and capabilities of Social Customer Service.
Contact Center Analytics – 5%
- Given a set of desired metrics, determine the appropriate reporting solution, taking into account data sources, data volume, and various contact center technologies (ACD, IVR, PBX, etc.).
- Given a scenario, evaluate the considerations when designing reports and dashboards to serve different stakeholders (agents, supervisors, managers, executives)
Integration and Data Management – 5%
- Explain the use cases and considerations for common Service Cloud Integrations.
- Explain the considerations for data migration and data quality.
Service Console – 15%
- Given a scenario, identify the appropriate Service Console features to meet the business need.
- Explain how different Service Console features work together to deliver business value.
- Given a set of business requirements, describe how a feature should be implemented.
General Setup Process
- Automate case management—First, route customer questions, comments, and feedback to the right people and places with as little work as possible. Analyze service metrics to spot trends and make better choices about service.
- Add multiple channels—Once your case management system is in place, engage with customers on their favorite communication tools, such as phones, emails, websites, social media, and more. Sync all your channels to a console so that your team can respond to customers anywhere.
- Capture knowledge—As customer engagement provides your team with insights, store all useful information in an easy-to-search Knowledge base so helpful articles are just a click away for support agents or customers.
- Expand efficiencies with AI—Finally, include artificial intelligence and bots to streamline more tasks and predict service before it’s needed.
Case Management Tools
| Case Management Tool | Description |
| Queues | Automatically prioritize your support team’s workload by creating lists from which specific agents can jump in to solve certain types of cases. |
| Assignment Rules | Automatically assign incoming cases to specific agents so that the right people work on the right cases. |
| Escalation Rules | Automatically escalate cases to the right people when the cases aren’t solved by a certain time. |
| Auto-Response Rules | Automatically send personalized email responses to customers based on each case’s details. |
| Page Layout Editor | Customize a case page’s contents, like the fields and buttons that appear on the page, along with what is visible to whom. Additionally, customize the structure of the page, and the position of its components, with the Lightning App Builder. |
| Email Templates | Create email templates to save time and standardize communications sent to customers from cases. Automate information on emails with merge fields. Templates are automatically available to anyone in the org. |
| Entitlement Management | Provide the correct level of support for customers. Define, enforce, and track service agreements and service contracts as part of an overall support management process. |
| Omni-Channel | Manage support agents’ priorities and their capacity to take on work items so that they’re given only the number of assignments that they can handle. Route all assignments to the correct agents so that they no longer have to choose work assignments manually from a queue. |
| Macros | Help support agents automatically complete repetitive tasks on cases, such as selecting the right email templates, so that they can spend time doing more important things. |
| Quick Text | Create predefined messages for support agents, like greetings, answers to common questions, and short notes to insert in cases, emails, web chats, and more. Save time and standardize on messaging to customers. |
| Utilities | Give support agents quick access to productivity tools, like notes, history, softphones, and more in the footer of the console. |
Interaction Channels
| Interaction Channel | Description |
| Web-To-Case | Admins use a Salesforce wizard to generate an HTML containing the desired case fields to collect so that the form can be used on the company’s website |
| Email-to-Case | Admins can create one or more Salesforce emails that generate a case when an email is received. |
| Call Center & Open CTI | Boost phone productivity by integrating Salesforce with third-party computer-telephony integration (CTI) systems. See Salesforce data for incoming calls, make outgoing calls directly from the console, and report on call outcome, duration, and more. |
| Self-Service Communities | Help customers find answers, log cases, and update orders on their own from web communities. Customize, create, and brand communities with easy-to-use templates, components, and apps. |
| Social Customer Service | Help support agents listen, respond, and log cases for customers on social platforms like Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, and more. Use keywords, classifiers, and language detection to make sure that agents find the right posts and work the right issues. |
| Chat & Embedded Service | Engage with customers browsing the web with real-time, live chat. Quickly embed unobtrusive chat capabilities on company websites for both desktop and mobile browsers to let customers chat with agents and deflect cases before they get logged. |
| Snap-ins for Mobile & SOS | Add service to mobile apps so that customers can get help from apps on phones and tablets. With an SDK (software development kit), developers can let customers create and manage cases, live chat with support agents, video chat and screen share with agents (SOS), and view knowledge base articles on the go. |
| Messaging | Engage with customers using messaging apps like SMS text and Facebook Messenger, so that they can connect with support agents instantly from anywhere. Help agents manage multiple text conversations at once and see each text alongside relevant Salesforce data. |
| Field Service | Support onsite visits out in the field with mobile solutions like job schedules, van inventory, and more—with or without web connections. |
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
Usually measured by a post-touch survey, this measures the overall satisfaction of customers after dealing with customer service. This can be measured as a percentage or as a number (usually 1-10). Source
Average Handle Time (AHT)
Tells managers how long it takes for their agents to complete a single conversation. Source
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Measures the likelihood that your customers will recommend your brand to others—an important characteristic of a pleased customer, which can lead to positive word of mouth. Source
First Contact Resolution (FCR)
Expressed as a percentage, this measures the proportion of cases that are solved on the first touch with customer service. Source
First Response Time (FCR)
This is the average amount of time it takes for customer service to initially respond to customer inquiries. Source
Total Cases
The sum total of cases that come through the contact center over a certain amount of time. Source
Service Console Productivity Tools
| Tool | Description | Great For… |
| Quick text | Quick text is a predefined message, like a greeting, note, phrase, or answer to a common question. Users can insert quick text in their emails, chats, and more. To insert quick text, users click a button or press a keyboard shortcut. | Standardization Replacement for copy/paste |
| Macros | A macro is a set of instructions that tells the system how to complete a task. Users can run macros to complete repetitive tasks—selecting an email template, sending an email to a customer, updating the case status—all in a single click. When a user runs a macro, the system performs each instruction on the open record. Users run macros from the app’s utility bar. |
Consistency Performing repetitive tasks |
| History | The History utility lets users see their recently visited records. Users can see their subtabs in context of the workspace tabs they’ve visited and copy links without opening the record. Users access the history from the app’s utility bar. | Viewing a list of recent records Sharing links |
| Mass quick actions | Mass quick actions let users edit up to 100 records from any list view, except for recently viewed lists. Users can only create and update records with mass quick actions. | Updating multiple records at the same time |
| Split view | Split view lets users open list views while still viewing record details. Split view displays in a collapsible column, so users can go back to viewing just the record in one click. Users can open or close split view from the vertical bar on the left-hand side of the console. | Context switching |
| Keyboard shortcuts | An email template is a predefined email. Depending on how you use it, users can customize the email before sending it, or it can be sent automatically as-is. You can automate information on emails with merge fields. Templates are automatically available to anyone in the org. You can insert email templates in: Email actions manually (in the publisher or global actions) Macros that include instructions for Email actions Predefined field values for the Email action Apex QuickActionDefaultsHandler interface |
Standardization Automation |
| Send email notifications | Various settings on the Support Settings page in Setup let you customize email notifications for users. You can set it up for agents to receive an email when the case owner changes and when case comments are added. Even contacts can receive email notifications when the case is created, updated, or comments are added. | Keeping agents and customers notified of updates |
| Predefined field values for Quick Actions | Predefined field values let you prepopulate a quick action with default field values. For example, in the Email action, you can automatically include Cc and Bcc recipients, add an email template, or ensure that emails are associated with Salesforce records. Predefined field values can be real click-savers. You can create a custom action called Close Case that has the Status field preset to Closed but also includes the Internal Comment field. That way agents can leave a comment at the same time. | Consistency Automation |
Macros
| Macro Type | Description |
| Regular macros | These macros perform actions that can be undone, meaning nothing is submitted, sent, or saved. For example, a macro that inserts an email template but doesn’t send the email is a regular macro. |
| Irreversible macros | These macros perform actions that can’t be undone, such as sending emails to customers or updating a case’s status. These macros contain a Submit Action instruction that’s irreversible. There’s also a special permission that allows users to work with them. To create, edit, or run macros that contain irreversible actions, the user must have the Manage Macros Users Can’t Undo permission.Users without the Manage Macros Users Can’t Undo permission can still create and edit macros that don’t contain instructions for performing irreversible actions. Just make sure they have create and edit permission on the macro object itself. |
| Bulk macros | These macros can run on multiple records at a time. |
Macro & Quick Text Sharing Models
| User Interface | Sharing Model |
| Lightning Experience | Share folders Let users organize and share quick text and macros in folders. To share an item, users add items to a folder, and then share that folder. To use this model, you enable folders for quick text and macros in Setup. Note: Keep in mind that sharing settings on folders override sharing settings on individual items. If you shared macros or quick text in Salesforce Classic, those settings are ignored after folders are enabled. After you enable folders for quick text or macros, we recommend that you move all existing items into folders and share those folders with your users. If an item isn’t in a folder, only the owner, creator, and admin have access. Also verify that your macro and quick text page layouts include the Folder field so that your agents can actually assign items to a folder. |
| Salesforce Classic | Share individual items Let users share quick text and macros individually. To share an item, users click the Share button on the quick text or macro record details. To use this model, you don’t have to enable anything because it’s the default behavior in Salesforce Classic. |
| Both | Share org-wide Let users see all quick text and macros in your org. To use this model, you update the org-wide sharing settings for the quick text and macros objects to public in Setup. We don’t recommend this model for most orgs. |
Agent Chat Productivity Features
| Feature | What It Does | Where to Enable It |
| Sneak peek | Lets the agent see what the visitor is typing before they hit Send. | Chat Configuration |
| Chat transfer | Lets agents transfer a chat to another agent or group of agents. | Chat Configuration |
| Quick Text | Lets you create standardized messages that agents can access during a chat. This saves them the trouble of typing out the same responses over and over, and it keeps your messaging consistent. | Quick Text in Setup |
| Push timeout | Routes the chat request to another agent when the first agent doesn’t accept or decline in a set number of seconds. | Omni-Channel Routing Configuration |
| Customer timeout | Ends the chat when the customer doesn’t respond in a set number of seconds. You can also display a warning before the chat ends to give them a chance to speak up. | Chat Button |
| Decline reasons | Lets agents select from a list of reasons when they decline a work request. | Omni-Channel Presence Configuration |
| Visitor blocking | Lets agents block a customer who’s spamming or otherwise violating your terms of service. | Chat Configuration |
Customer Chat Productivity Features
| Feature | What It Does | Where to Enable It |
| File transfer | Lets agents request a file from the customer during a chat. For example, a customer can send an image of their broken solar panel to help the agent identify which part they should send. | Chat Configuration |
| Proactive chat invitations | Provides an animated chat invitation that appears based on certain criteria. For example, if the customer moves their mouse toward the Close button on their browser, or when the customer reaches $100 in their shopping cart. | Chat Button, Embedded Chat Settings |
| Fill in pre-chat fields | Saves customers from having to type out information that you already know, like their name. This only works if your customers have to log into your website or Community. | Embedded Chat Settings |
| Queue position | Displays the customer’s place in line while they wait for an agent. | Chat Button, Embedded Chat Settings |
| Lightning components for various chat states | Lets you fully customize your chat window’s appearance with Lightning Components. | Developer Console |
Embedded Service SDK for Mobile Apps
It’s a set of tools to help build essential Service Cloud features into your iOS or Android app. It helps bring the features of Knowledge, Case Management, and Chat into the app. Source
Omni-Channel
Salesforce uses the terms work and work items to refer to all the different types of Salesforce records that Omni-Channel routes, such as cases, leads, web chats, custom objects, and more. Omni-Channel takes incoming work items and routes them to the most qualified, available support agents using the routing criteria that you define.
Source
Routing Frameworks
| Type of Routing | How It Works | Best Use Case |
| Queue-based routing | You assign agents to queues, which typically represent a single skill. Omni-Channel assigns work items to a queue and then pushes work items to an agent who is a member of that queue. Works natively in Salesforce. |
Best for smaller organizations that support a limited number of products. |
| Skills-based routing | You assign skills to agents and required skills to work item types. Omni-Channel matches work items to agents who possess all the required skills. Works natively in Salesforce. |
Best for larger organizations that: – Have many agents that support many products. – Support products that require complex skill sets. – Support customers in many countries or across multiple languages. |
| External routing | A third-party routing implementation of your choice routes work items through Omni-Channel to agents via the Salesforce Service Console. A developer uses APIs to integrate the partner routing application with Salesforce. |
Best for organizations that want to route work to the Salesforce Service Console while keeping the routing implementation that the organization currently uses. |
Queue-Based Routing
Omni-Channel uses three factors to prioritize a work item:
- Priority. First, it considers the priority of the queue from which the work item came.
- Wait Time. Next, it considers the amount of time the work item has been waiting in the queue.
- Available Agents. Finally, it considers the members of the queue who are available to receive new work items.
Snap-Ins & SOS
Social Media With Social Customer Service
Data Model
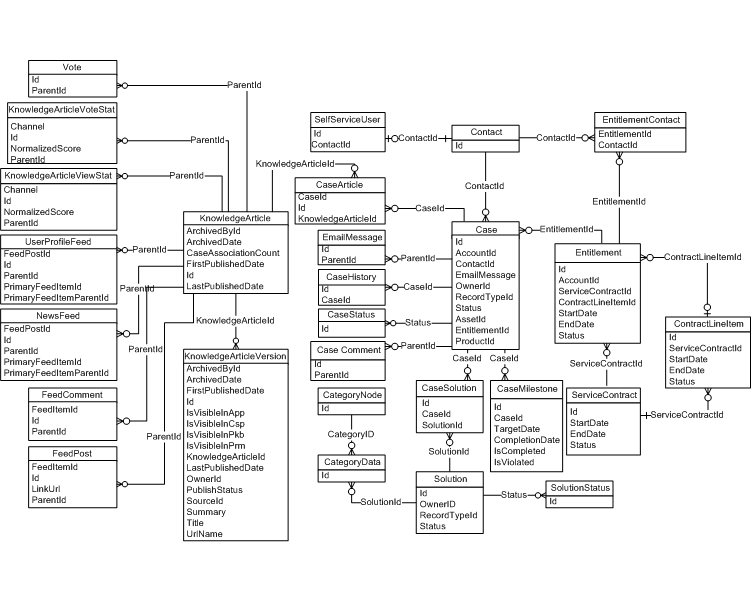
Resources
- Exam Guide
- Chris Gardner’s Service Cloud Consultant Resource Guide
- Asagarwal Service Cloud Study Guide
- Trailhead – Service Cloud Consultant Prep Trailmix
- Trailhead – Service Cloud Specialist Superbadge
- Trailhead – Salesforce Mobile App Customization
December 05, 2020 at 01:33AM
Click here for more details...
=============================
The original post is available in Blog by Luke Freeland
this post has been published as it is through automation. Automation script brings all the top bloggers post under a single umbrella.
The purpose of this blog, Follow the top Salesforce bloggers and collect all blogs in a single place through automation.
============================

Post a Comment